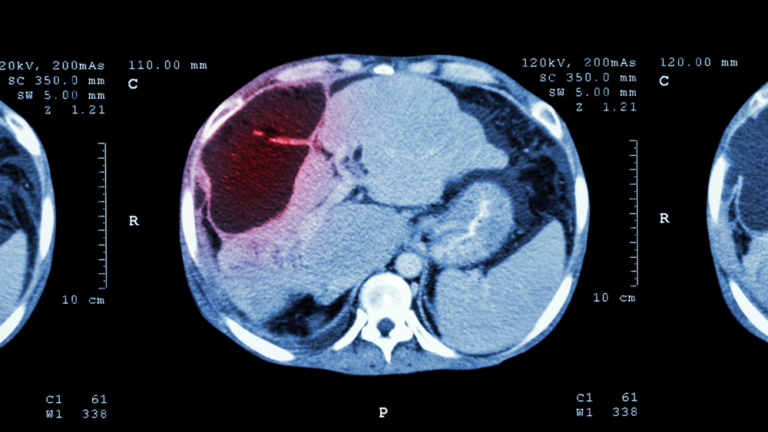
What Are Hemangioma Liver Lesions
Hemangioma liver lesions are noncancerous, abnormal masses of tangled blood vessels found in the liver. Also referred to as hepatic hemangiomas and cavernous hemangiomas, a liver hemangioma will typically occur as a single collection of abnormal vessels. In rare cases, they may form as a group or cluster.
DocPanel is committed to making sure every patient receives excellent care. If you would like an expert second opinion on a liver lesion diagnosis from one of our subspecialty radiologists, you can learn more here.
How Common Are Hemangioma Liver Lesions
Liver hemangiomas are the most common type of benign liver lesion.
It is estimated that around 5 percent of adults in the United States have small hemangiomas in their liver.
While hemangioma liver lesions themselves do not pose a threat, they do present a diagnostic challenge. Hemangiomas share similar characteristics to other liver lesions, and are commonly mistaken for malignant hyper vascular tumors of the liver, such as hepatoma (hepatocellular carcinoma) and fibrolamellar carcinoma. To prevent misdiagnosis, radiographic images with suspicious findings should be read by a subspecialty radiologist. Appropriate patient management planning relies heavily on a radiologist’s familiarity with differentiating liver lesions.
How Are Hemangioma Liver Lesions Detected
Hemangioma liver lesions are detected through imaging studies. Because hemangiomas are typically asymptomatic, they are most often discovered incidentally – usually during an ultrasound. After the initial detection of a liver lesion, CT and MRI scans are used to further evaluate the type and size.
In order to accurately characterize and differentiate hemangiomas from other tumors, it is imperative scans are interpreted by a subspecialty radiologist with extensive experience in abdominal imaging. A second opinion can also help confirm a diagnosis and prevent mistreatment. In cases where imaging studies are inconclusive, a biopsy may be performed to rule out malignancy. Biopsy, however, should be avoided whenever possible due to the high risk of hemorrhage in hemangiomas.
Hemangioma Liver Lesion Symptoms
Generally, hemangiomas in the liver are asymptomatic. In rare cases, if a hemangioma grows to be large, it may cause abdominal discomfort. In such instances, an individual might experience:
- Pain in the upper right abdomen
- Feeling of being full without eating
- Nausea or vomiting
How Are Hemangioma Liver Lesions Treated
Benign hemangioma liver lesions generally do not require any treatment. In cases where the mass grows large to the point of discomfort, treatment may be required. However, the risk of rupture is very low, so surgical removal is not typically advised. There is no evidence that a liver hemangioma can lead to liver cancer.
Risk Factors
Studies show that the hormone estrogen may play a role in the growth of hemangioma liver lesions. Patients diagnosed with a liver hemangioma may be advised to avoid medications that alter hormone production, such as birth control pills.
Get a Subspecialty Second Opinion Today
The DocPanel platform enables people all over the world to get an expert second opinion in as little as 24 – 72 hours.
An easy 3-step process – instantly upload your scans, select an expert subspecialty radiologist (or have DocPanel assign your case to the appropriate subspecialist), and submit your request. Upon uploading your scans, you’ll also have the opportunity to ask any questions you might have about your case.
Not sure what a subspecialist is? Learn more with our in-depth article on the importance of getting a second opinion from a subspecialty radiologist.
Dr. Richard Semelka, leading expert in abdominal imaging, has been practicing radiology for over 28 years. He’s written over 16 text-books, 370 peer-reviewed papers, and has over 21,000 research citations in Abdominal Imaging.
Get your scans interpreted by Dr. Semelka or explore DocPanel’s complete team of subspecialty radiologists. Request a second opinion today.